
I agree Our site saves small pieces of text information (cookies) on your device in order to deliver better content and for statistical purposes. You can disable the usage of cookies by changing the settings of your browser. By browsing our website without changing the browser settings you grant us permission to store that information on your device.
See our Anatomopathology dedicated page to explore all our available tests.
The measurement of various blood metabolites, ions, and enzymes provides a primary screen for function of major metabolic organs such as kidney, liver, gastrointestinal tract, as well as for lipid and glucose homeostasis.
A panel of parameters is proposed, including:
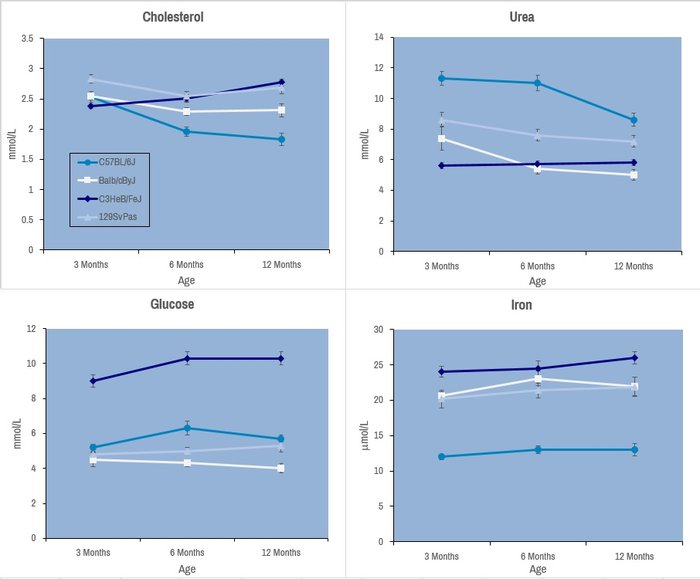
Selected plasma chemistry data from female mice (N=20 per line) of common laboratory strains at different ages (Champy et al. Mammalian Genome 2008). Error bars reflect ± SEM.
These tests are performed with an AU-480 automated laboratory work station (Beckman Coulter France SAS, Villepinte, France).
Food consumption is measured by manually weighing remnants of food in the feeders. The test gives precise or estimated evaluation of energy intake in mice depending of whether the animals are singly or socially housed. Food consumption (and water consumption) may also be assessed more accurately in metabolic cages or in polymodal indirect calorimetry monitoring system.
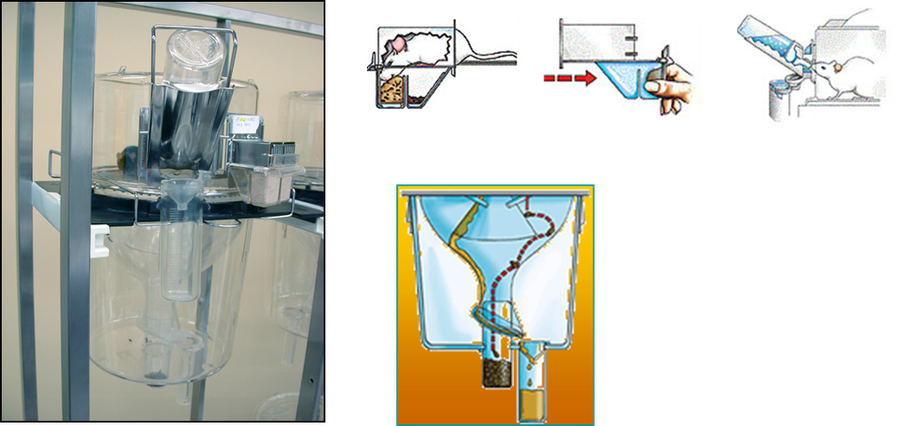
Renal function may be assessed by metabolic cages. Metabolic cages allow separate collection of urine and feces. The mouse is confined in an enclosure with a wire grid floor for up to 72 h. In parallel, food and water intake are recorded daily by weighing the food and water containers.
Renal function may be evaluated through the measurement of clinical chemistry parameters in 24 hours urine collection. Some models of renal failure / hypertension could be proposed to test drugs.
Feces are collected for the measurement of heat loss by calorimetric bomb.
Metabolic and diuresis cages (Line 3, Techniplast).
8 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
24 hours urine are collected in metabolic cages (Techniplast) for the evaluation of renal function.
The following parameters: Na, K, Cl, glucose, urea, creatinine, total proteins, albumin, calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), are measured in plasma and urine.
Plasma and urine osmolarity can be determined on an Osmometer (Fiske associates).
Creatinine clearance and fractional tubular Na re-absorption are calculated.
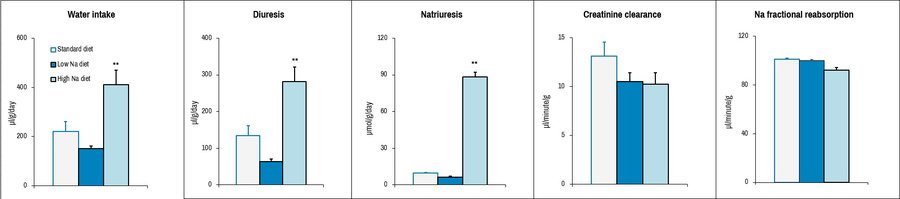
Selected parameters from metabolic cage collection used to analyse renal function of C57BL/6J mice upon provision of diets with different sodium (Na) content. Standard diet = 0.25% Na+; Low Na diet = 0.03% Na+; High Na diet = 3% Na+. Error bars reflect ± SEM.
Urine is collected over 24h in metabolic cages (Techniplast, France).
Urine chemistry is performed on an AU-400 automated laboratory work station (Beckman Coulter France SAS, Villepinte, France).
Urinary albumin is measured by ELISA.
Analysis can be done on “spot urine” or on urine collected in metabolic cages.
To evaluate renal function, analysis of urine collected over 24 hours must be performed in parallel with plasma.
We can procure and provide a high fat diet for obesity, diabetes and steatosis induction. Normally this challenge is most effective in male mice and proceeds for approximately 15 weeks for full effect of challenge.
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
We can procure and provide a high sodium diet for vascular, renal, and cardiac challenges.
Ultrasound visualizaton of kidneys for non-invasive assessment of tumor growth, mineralization, or cysts.
See our Gene expression analysis dedicated page to explore our different related tests.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)
We can procure and provide a high fat diet for obesity, diabetes and steatosis induction. Normally this challenge is most effective in male mice and proceeds for approximately 15 weeks for full effect of challenge.
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
We can procure and provide a high sodium diet for vascular, renal, and cardiac challenges.

Selected parameters from metabolic cage collection used to analyse renal function of C57BL/6J mice upon provision of diets with different sodium (Na) content. Standard diet = 0.25% Na+; Low Na diet = 0.03% Na+; High Na diet = 3% Na+. Error bars reflect ± SEM.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)