
I agree Our site saves small pieces of text information (cookies) on your device in order to deliver better content and for statistical purposes. You can disable the usage of cookies by changing the settings of your browser. By browsing our website without changing the browser settings you grant us permission to store that information on your device.
See our Anatomopathology dedicated page to explore all our available tests.
The measurement of various blood metabolites, ions, and enzymes provides a primary screen for function of major metabolic organs such as kidney, liver, gastrointestinal tract, as well as for lipid and glucose homeostasis.
A panel of parameters is proposed, including:
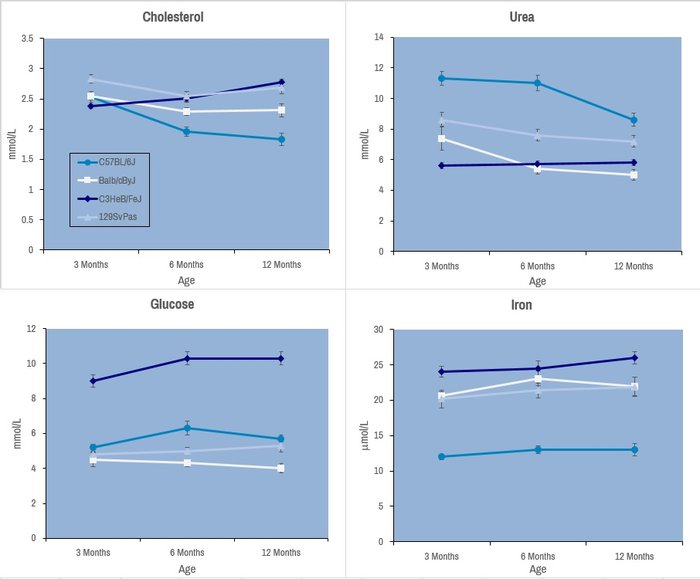
Selected plasma chemistry data from female mice (N=20 per line) of common laboratory strains at different ages (Champy et al. Mammalian Genome 2008). Error bars reflect ± SEM.
These tests are performed with an AU-480 automated laboratory work station (Beckman Coulter France SAS, Villepinte, France).
Body composition for fat, lean and free body fluid is evaluated on conscious mice by quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance on Minispec analyzer.
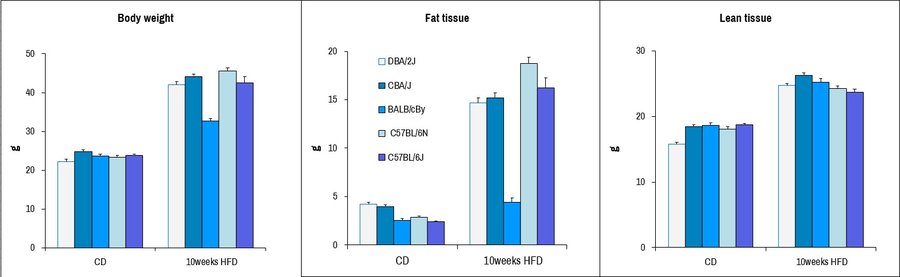
Body composition analysis of male mice from different common laboratory strains after provision of chow diet (CD) or 10 weeks provision of high-fat diet (HFD), including complete body weight, fat tissue content, and lean tissue content. Dramatic increases in fat tissue is seen upon HFD-diet treatment for most strains excepting BALB/c, consistent with what has previously been reported.

Body composition is evaluated by Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) using Minispec+ analyzer (Bruker BioSpin S.A.S., Wissembourg, France)
The energy content of stools is evaluated in a bomb calorimeter (C503 control, IKA).The assay provides the energy digested by mice and then indirectly the intestinal function. The energy digested is calculated by the difference between the total calories ingested and excreted in faeces.
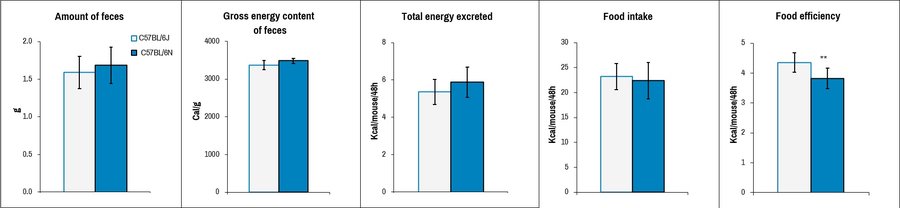
Analysis of parameters in bomb calorimetry demonstrates increased food efficiency in C57BL/6J mice compared to C57BL/6N mice.

C5000 Bomb Calorimeter (IKA, Staufen, Germany).
The tolerance to cold stress evaluates thermoregulation.
Mice are housed in individual cages during 6 hours at 4°C in a cold room. Body rectal temperature is measured with a probe every hour on each mouse.
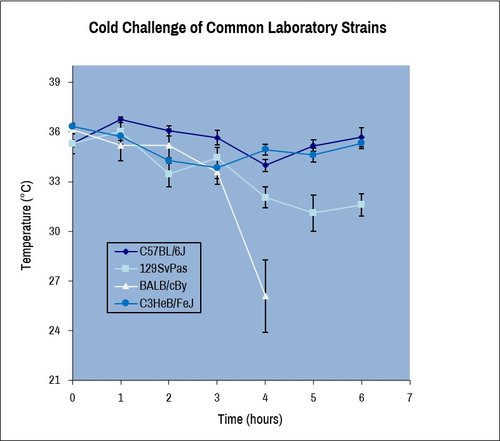
Cold temperature challenge of male mice from different common laboratory strains demonstrates strain-dependent thermoregulation response.
Food consumption is measured by manually weighing remnants of food in the feeders. The test gives precise or estimated evaluation of energy intake in mice depending of whether the animals are singly or socially housed. Food consumption (and water consumption) may also be assessed more accurately in metabolic cages or in polymodal indirect calorimetry monitoring system.
Exercise performance is assessed by treadmill exercise using a defined protocol with increase in speed and incline until exhaustion. The duration of running and the total distance covered evaluates the performance of the mice.
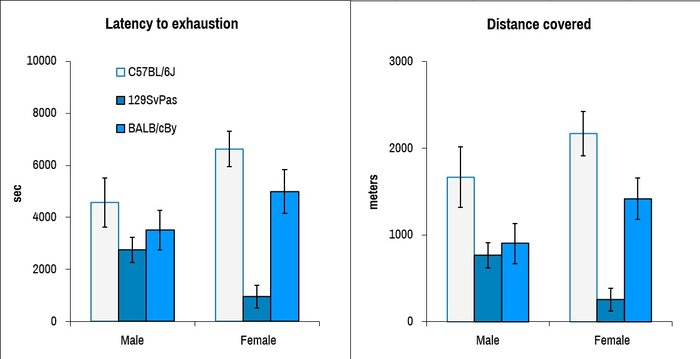
Forced exercise performance of male and female mice of three common laboratory strains were assessed at a constant speed. The results are expressed as a function of time (latency) or distance.

Treadmill device for mice (5 lanes) (BIOSEB, Vitrolles, France).
See our Glucose homeostasis dedicated section to explore our available tests.
See our Immunoprofiling dedicated page to explore all our available tests.
Measurement of lipids levels in the liver including total cholesterol, triglycerides and free fatty acids.
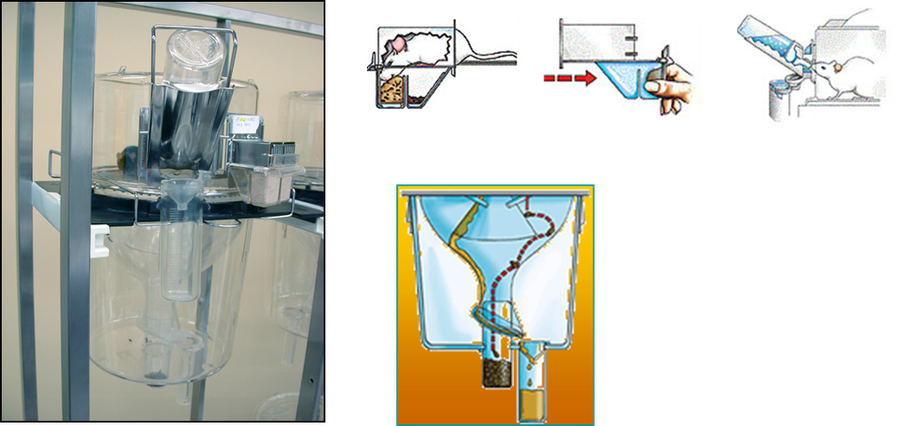
Renal function may be assessed by metabolic cages. Metabolic cages allow separate collection of urine and feces. The mouse is confined in an enclosure with a wire grid floor for up to 72 h. In parallel, food and water intake are recorded daily by weighing the food and water containers.
Renal function may be evaluated through the measurement of clinical chemistry parameters in 24 hours urine collection. Some models of renal failure / hypertension could be proposed to test drugs.
Feces are collected for the measurement of heat loss by calorimetric bomb.
Metabolic and diuresis cages (Line 3, Techniplast).
8 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
Calorimetry cages allow the simultaneous measurement of energy expenditure, ambulatory activity as well as food and water intake. Energy expenditure is evaluated through indirect calorimetry by measuring oxygen consumption with an open flow respirometric system. It also monitors CO2 production, thus the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) and finally heat production can be calculated. Infra-red frames are integrated to the system in order to measure ambulatory activity. A food intake monitoring system is also integrated for the measurement of feeding / drinking behaviors.
Polymodal indirect calorimetry at different temperature: altered temperature is one of the most basic metabolic challenges available. By positioning our indirect calorimetry cages in an insulated, temperature-regulated environment, we can perform cold and heat challenges with polymodal measure of body temperatures, activities, and heat.
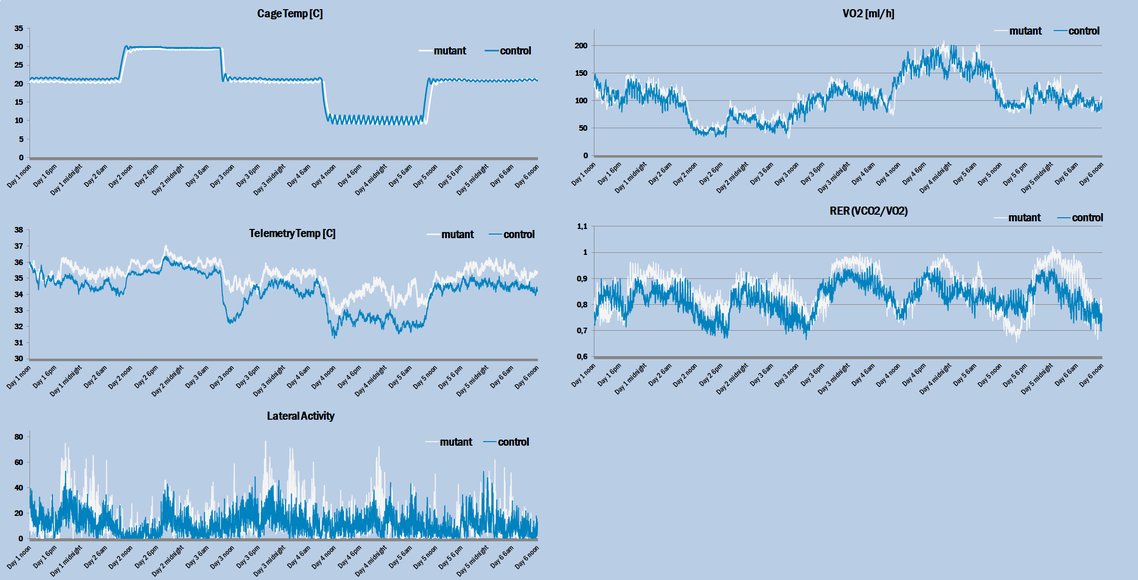
Sample experimental data for comparison between mutant (grey) and control (blue) mice (N=5 per group) at 20°C, 30°C, and 10°C thus defining the impact of elevating and reducing ambient temperature. Cage temperature, peritoneal temperature (by telemetry), lateral activity, and gas measures were collected for each minute across several days.

Home cage system Phenomaster/Labmaster (24 cages) (TSE LabMaster systems GmhB, Bad Homburg, Germany).
The High-Resolution Digital Radiography system (Ultrafocus by Faxitron) gives very precise images of the skeletton. Analysis of the digital X-ray pictures is generally performed with respect to bones from the head (zygomatic bone, maxilla, mandibles), teeth, scapulae, clavicle, ribs (number, shape, fusion), pelvis, vertebrae (numbers, shape and potential fusion of cervical, thoracic, lumbar, pelvic and caudal ones), limb bones (humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia), joints, digits and syndactylism.
In dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry mode (DXA), the system measures bone mineral density (BMD) and also determine lean and fat mass percentages.
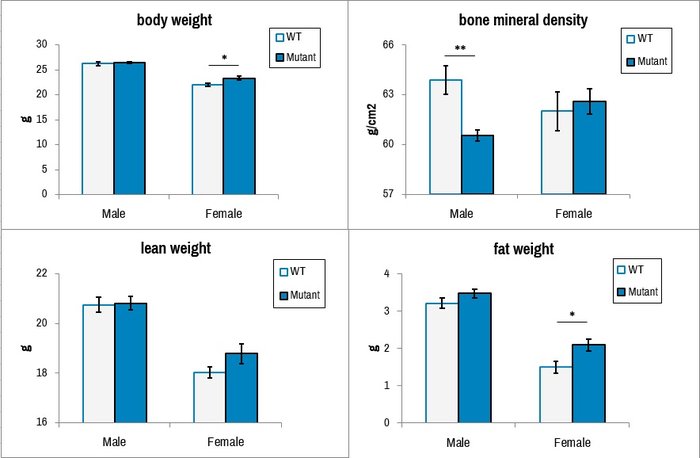
Comparison of wild-type C57BL/6N (WT) and Ttc39a deletion (Mutant) mice for noted body composition parameters by non-invasive Ultrafocus DXA imaging. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01.
We can procure and provide a high fat diet for obesity, diabetes and steatosis induction. Normally this challenge is most effective in male mice and proceeds for approximately 15 weeks for full effect of challenge.
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
We can procure and provide a high sodium diet for vascular, renal, and cardiac challenges.
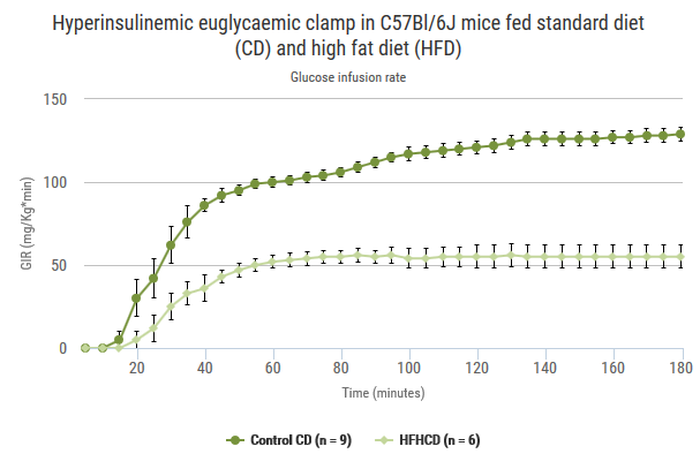
Alterations in insulin sensitivity (resistance or hypersensitivity) can be revealed on the basis of an insulin sensitivity test. However a more reliable quantitative analysis is performed using the Euglycaemic Hyperinsulinemic clamp technique. In this procedure insulin is administrated to raise plasma insulin concentration while glucose is infused to maintain euglycaemia. The glucose infusion rate needed to maintain euglycaemia is a reflection of insulin action in the whole body when both glycemia and hyperinsulinemia are set at constant. A femoral vein catheter is placed under anaesthesia 3 days prior to the experiment. The test is conducted on 5h-fasted vigil and not restrained mice.
The glucose tolerance test is commonly used to assess the ability of standardized glucose bolus to induce hyperglycaemia. The glucose is either administrated by oral gavage or by intra peritoneal injection. The blood glucose level is measured at different time points after administration.
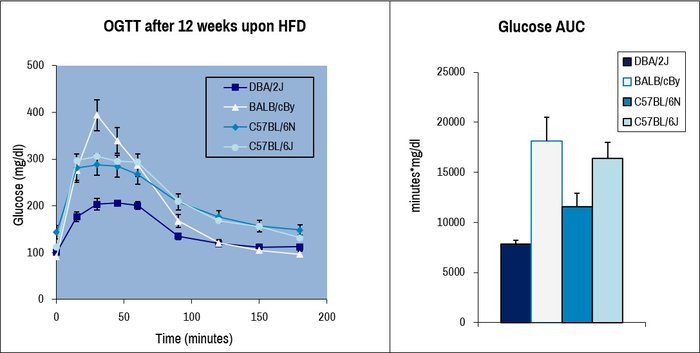
Oral glucose tolerance tested on male mice of four common laboratory strains after provision of high-fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks. Evolution of blood glucose over time (left panel) and glucose area-under-the-curve (AUC) summaries detect strain-specific difference in HFD response and glucose tolerance.
The insulin sensitivity test is used to measure the regulation of the glycemia by the whole body after injection of a standardized insulin load. Blood glucose is measured at different time points over 90 minutes after the administration using blood glucose monitor and glucose test strips.
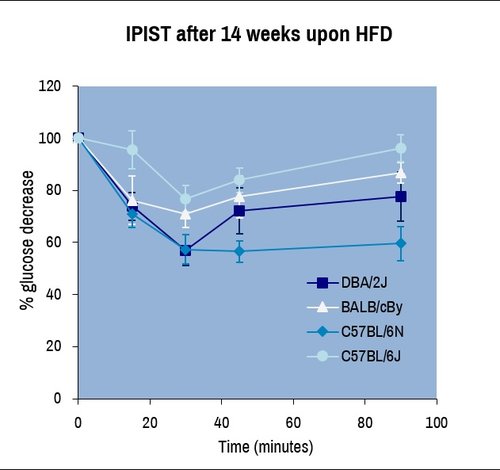
Intraperitoneal-administered insulin sensitivity tested (IPIST) on male mice of four common laboratory strains after provision of high-fat diet (HFD) for 14 weeks. Evolution of blood glucose over time detect strain-specific difference in HFD response and glucose homeostasis.
Identification of specific bacterial loads present in the feces of mice by virtue of quantitative ribosomal 16S DNA sequencing.
For more details, please see our Microbia profiling dedicated section.
Core body temperature is affected by numerous physiological changes including systemic inflammation, altered nutrient consumption, and physical exertion. Due to circadian changes in body temperature, it is important to measure at regular times of day.
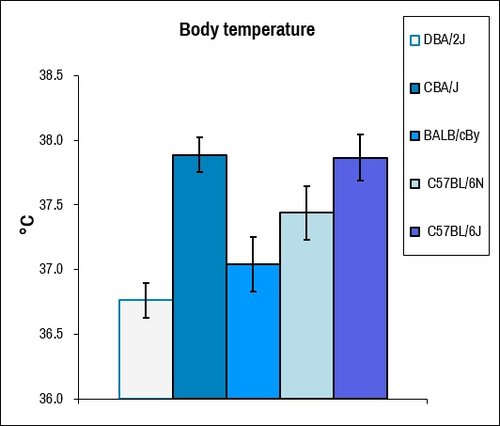
Comparison of core body temperature between males mice (N=7) of commonly used laboratory strains determined by digital rectal thermometer.
See our Gene expression analysis dedicated page to explore our different related tests.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)
Controlling infectious diseases requires understanding of the relationships between immune cells and pathogens.
Most current studies to understand infectious processes rely on models requiring
The Biosafety Level 3 Containment Facility (BSL3) has special engineering and containment features that allow investigators to work safely with pathogens classified as risk group 2 or 3. This facility consists of three laboratory suites corresponding to an animal housing room, a laboratory for in vitro experiments and a bio-imaging area.
All instruments are accessible to trained users based on the scientific and regulatory rules established by scientific and biosecurity and safety manager of BSL3. Although the BSL3 platform was only fully operational in May 2015, it already permitted to set up
Real-time imaging studies of immune responses in mice challenged by pathogens such as Salmonella or Brucella infection have led to the development of an immunophenotyping analytical pipeline devoted to infection in synergy with our Immunophenotyping module. The analysis of organ distribution of biomolecules engineered to transport and deliver nucleic acids on living animals using an IVIS Lumina III device is also developed in the frame of a contract with a biotech company. Therefore, we can visualize the spread of infection in vivo, isolate and characterize the pathogens, and analyze phenotypic and functional modification of immune system in the course of infections by advanced live-imaging and flow and mass cytometry.
We provide a broad range of instruments and services for academic and industrial customers. An experienced staff of scientists, technical experts and instrument specialist provides instructions for the design, execution and analysis of standardized multiparametric flow, spectral, mass cytometry and advanced microscopy based studies. All these cutting-edge equipment are technically and operationally enrolled in a regular maintenance program with their commercial providers. Moreover, instrument specialists at PHENOMIN are dedicated to the maintenance and tuning of the instruments on a daily basis. The characterization of the cytometer status and performance using CS&T beads for cytometer set up and tracking system, ensure reproducible performance and instrument sensitivity on a day to day basis. All experiments are standardized using applications setting in order to achieve: (1) high consistency of results over time and (2) facilitate data analysis and results validation. All data are archived and stored on dedicated servers. Depending on the technical complexity and availability, the equipment can be handled by our experts or made available for use to trained customers. PHENOMIN has set up an on line instrument tutorial for training external users. PHENOMIN applies two types of price: one for its academic clients on full cost basis and the other one for its industrial customers taking into consideration intellectual property and the transfer of know-how.
Real-time imaging studies of immune responses in mice challenged by pathogens (Salmonella infection model) and infection-immunophenotyping analysis pipeline in synergy with immunophenotyping CIPHE facility.
Set up vaccine assays and test the ability of adjuvants to enhance vaccine efficacy in a mouse model of infection.
We perform multi-derivation ECG heart in anesthetized mice with 8 probes to generate information about how the electrical activity propagates in 3 dimensions and to determine the electrical axis of the heart. Axis deviations may result from cardiac injury or from a congenital defect.
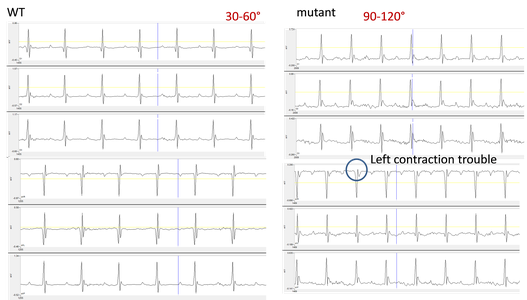
Electrical heart axis difference and specific electrical transmission issues are determined by multiderivational ECG. Multiderivational ECG profiles of a wild-type mouse (left) and mutant mouse (right). Deviated profiles in the mutant animal suggest a left-heart contraction deficiency as well as rotation of the electrical axis to 90-120⁰ from the normal 30-60⁰.
Any strain background can be used
Electrocardiograph ISO DAM8 amplifier (World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, USA) with ECG AUTO v3.3.5.5 (Emka technologies, USA) and 8 lead positions probes.
We recommend 6 mice per group minimum in same anaesthesia conditions and probes positions
Bioluminescence imaging is based on the detection of light emitted as a result of an enzymatic reaction involving a couple “enzyme / substrate”, usually “luciferase / luciferin”. When the enzyme is introduced into systems that are not naturally bioluminescent (cells, bacteria, transgenic animals), these systems play the role of reporter gene and allow to address many biological issues such as gene expression, cell proliferation (cancer) or bacterial dissemination (infectious diseases), for example. A dedicated camera collects emitted photons and the signal is processed to obtain images.
Bioluminescence is performed with IVIS Lumina systems and can be carried out under BSL3 conditions.
Some examples of applications :
IVIS Lumina III (Perkin Elmer)
Fluorescence is based on the excitation of a fluorophore then detection of emitted light. The incident light illuminates the fluorophore with one given wavelength that in return emits photons of longer wavelengths. Thus, fluorescence imaging needs a light source to excite the fluorophore within the targeted tissue, combined with a spectral filter to select the excitation wavelength, a second filter that only allows passage of the emitted fluorescence and finally a detector that detects the signal.
Fluorescence is performed with IVIS Lumina systems as planar epi-fluorescence mainly in the near infra-red wavelengths. Imaging can be performed in vivo (superficial foci) or ex vivo (organs).
Some examples of applications:
Determination of systolic blood pressure and heart rate in conscious mice by tail-cuff method.
Two apparatus of BP-2000 seriesII 6 channels (Visitech Systems, Apex, North Carolina, USA)
Number of animals: 9 mice/gender/genotype . Maximum age : 8 weeks
The X-Ray system gives very precise images of the skeletton. In DXA mode it automatically calculates BMD, BMC, and lean and fat mass percentages.

pDEXA Sabre (Norland)
The Apoe targeted mutation mice (Apoe -/-) are unable to produce apolipoprotein E which is essential for the transport and metabolism of lipids. These mice have a markedly altered plasma lipid profile compared to normal mice, and rapidly develop atherosclerotic lesions. A diet high in fat and cholesterol increases the incidence of atherosclerosis in these mice and this model is a useful model especially for pharmacological studies.
Mice deficient in low density lipoprotein receptor (Ldlr) have an elevated serum cholesterol level and display very high levels when fed a high fat diet. This model is also commonly used for hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis research.
Tests proposed:
The tolerance to cold stress evaluates thermoregulation.
Mice are housed in individual cages during 6 hours at 4°C in a cold room. Body rectal temperature is measured with a probe every hour on each mouse.

Cold temperature challenge of male mice from different common laboratory strains demonstrates strain-dependent thermoregulation response.
We can procure and provide a high fat diet for obesity, diabetes and steatosis induction. Normally this challenge is most effective in male mice and proceeds for approximately 15 weeks for full effect of challenge.
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
We can procure and provide a high sodium diet for vascular, renal, and cardiac challenges.
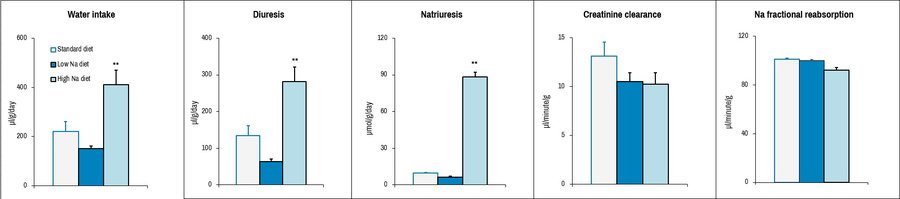
Selected parameters from metabolic cage collection used to analyse renal function of C57BL/6J mice upon provision of diets with different sodium (Na) content. Standard diet = 0.25% Na+; Low Na diet = 0.03% Na+; High Na diet = 3% Na+. Error bars reflect ± SEM.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)