
I agree Our site saves small pieces of text information (cookies) on your device in order to deliver better content and for statistical purposes. You can disable the usage of cookies by changing the settings of your browser. By browsing our website without changing the browser settings you grant us permission to store that information on your device.
The active avoidance test assesses cued evasion of an aversive stimulus. The mouse is trained during the acquisition period to escape the aversive stimulus, after which the extinction of the trained behaviour is measured. We offer varied acquisition and extinction periods to fit your needs and budget. Locomotion, severe vision and other sensory defects can effect this test.
C57BL/6N mice treated with scopolamine or vehicle prior to training. Scopolamine-treated animals do not improve cued responses indicating a failure to learn.
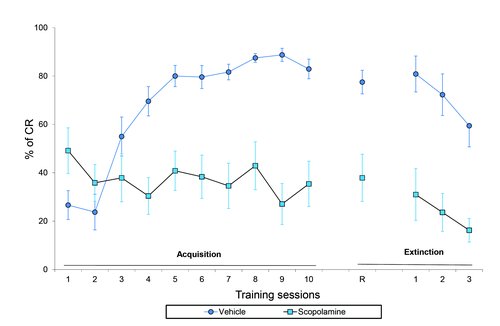
Scopolamine treatment prior to active avoidance testing inhibits learning. Evolution of cued responses (% of CR) in C57BL/6N mice during acquisition and extinction phases of active avoidance. Retention test (R) occurs 17 days after final acquisition session. Sessions in extinction phase are performed without aversive stimulus. Data points reflect Mean ± SEM (n=12).
Automated shuttle boxes (PanLab, Spain)
12 animals per group are recommended for reliable data analysis (alpha=0.05, beta=.2, D=1, Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test).
This is an associative learning paradigm for measuring emotional learning and memory. A neutral conditioned stimulus (CS, tone) is paired with an aversive unconditioned stimulus (US, foot-shock). After conditioning, the CS or the spatial context alone elicits a central state of fear expressed as reduced locomotor activity or total lack of movement (freezing).
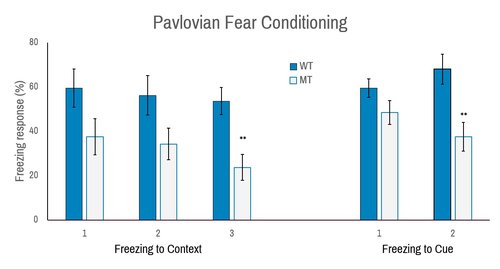
Comparison of wild-type (WT) and Atp6ap2 brain-specific deletion (MT) in fear-conditioning response as described in Dubos et al. (2015). Mutant mice are show reduced freezing to context and to cue. **, p<0.01.
Dubos, A. et al. Human Mol Genet. 2015. 24(23):6736-55.
4 automated cages (Coulbourn Instruments, Whitehall, USA)
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
Mice are social creatures and develop in group settings but most learning and behavioral tasks are limited to individual mice. IntelliCages allow cognitive and behavioural evaluation in a social environment using transponder technology, which also drastically reduce human involvement at the time of study.
This test is used to evaluate spatial reference memory in rodents. Mice are trained to escape from water by swimming to a submerged platform using only distal extra-maze cues.
2 rooms dedicated to water maze test and videotracking systems are used (Ethovion, Noldus)
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
The object recognition task is based on the natural tendency of rodents to explore a novel object / environment in comparison to a familiar one. This test allows evaluation of recognition memory to characterize potential memory defects.
Automated openfield arenas (Panlab, Barcelone, Spain) and different objects (marble, dice…) are required.
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
Object recognition and object location are based on the natural tendency of rodents to explore a new object / environment as compared to a familiar one. These protocols allow evaluation of working / recognition memory.
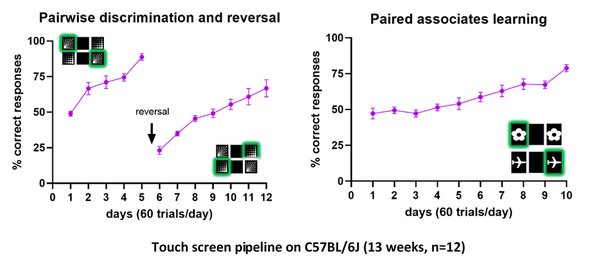
Touchscreen technology allows to explore cognitive deficits with a platform that is translatable across rodents, non-human primates and human subjects (Palmer et al., 2021) lending itself to a high degree of standardization and throughput.This methodology is low stress, using appetitive rather than aversive reinforcement.


In addition to the traditional behavioral tests used to study cognitive skills, such as novel object recognition, Morris water maze, and fear conditioning, PHENOMIN-ICS has implemented a touchscreen pipeline to assess visual discrimination, cognitive flexibility, and spatial learning.
After pre-training to learn to press an image that appears on the screen in order to obtain a reward of sweet water, the mice are tested in 3 different protocols.
12 Mouse Touch Screen Systems (Campden Instruments)
Strawberry syrup
12 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
This test allows evaluation of working memory. When placed in the Y-maze, mice tend to alternate visits between the three arms. A mouse with impaired working memory cannot remember which arm it just visited and thus shows decreased spontaneous alternation.
Home-made equipment made of PVC.
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
See our Anatomopathology dedicated page to explore all our available tests.
See our Gene expression analysis dedicated page to explore our different related tests.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)