
I agree Our site saves small pieces of text information (cookies) on your device in order to deliver better content and for statistical purposes. You can disable the usage of cookies by changing the settings of your browser. By browsing our website without changing the browser settings you grant us permission to store that information on your device.
The cardiovascular platform is designed to detect major cardiac phenotypes and indicators of cardiac diseases. Through in vivo evaluation of cardiovascular function we are able to detect congenital heart disease, systolic and diastolic dysfunctions, myocardial infarction, intracardiac shunting, valvular disease, cardiac hypertrophy and dilatation, aberrant conduction, arrhythmias, hypertension and hypotension. We can also propose sensitized pathological models to help reveal pathological phenotypes or for preclinical compound testing.
The lung function analysis platform provides evaluation of strain-, sex-, and gene-specific differences in breathing patterns. Using normal developmental conditions as well as different inflammatory stresses, we can use the lung as an organ system for first-line study of inflammatory sensitization or resistance.


Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis requires 14 days after a single administration to see significant airway fibrosis as well as associated inflammation. Effects are monitored by whole body plethysmography.
Exploration of lung inflammatory cells and mediators, e.g. cytokines, contained in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL). The service includes either the use of standard cytokines and chemokines techniques (Luminex, Elisa) or application of specific protocols provided by users.
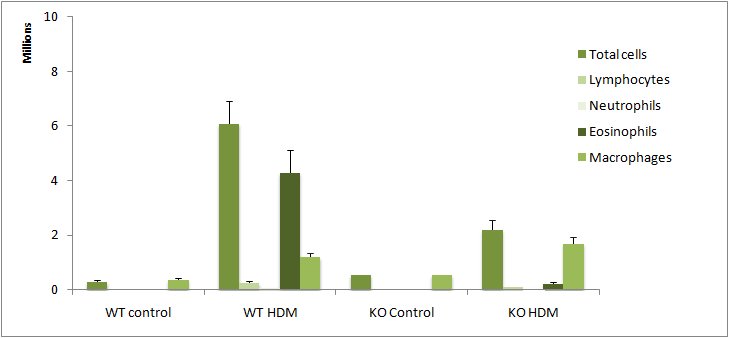
Lung inflammatory cell content in bronchoalveolar lavages (BAL) in House Dust Mite (HDM) model: WT/KO study (C57BL/6 background)
Advia 120 (Siemens AG, Erlangen, Germany)
Cytospin 4
Number of animals: 8 mice/gender/genotype
The intranasal instillation of 3U of elastase is sufficient to establish a meaningful multifocal emphysema in the lungs of mice C57BL6/N after 14 days. This can currently be evaluated by flexiVent™, microCT, and histology.
Non-invasive tracking of emphysema or tumor growth using computed tomographyic X-ray imaging.
Assessment of airway responsiveness to metacholine-induced brochoconstriction challenge in conscious mice by whole-body barometric plethysmography.
Plethysmography (Penh) allows determination of airway volumes, breath frequency and assessment of airway obstruction in non-restrained mice. This test allows evaluation of fibrosis, as well as physiological and anatomical defects of lungs (e.g. emphysema).
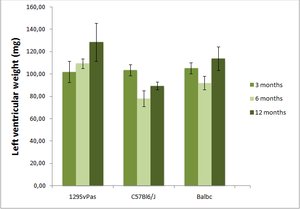
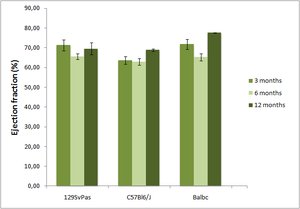
Echocardiography is considered the first-line diagnostic test, from which subsequent imaging or interventions can be recommended.
The Vevo 2100 High-Frequency Ultrasound Systems have been developed specifically for use in small animal imaging and are ideally suited for mouse or rat echocardiography. With center operating frequencies ranging from 15MHz to 50MHz one imaging system can be used to assess cardiac function from embryo to adult in many commonly used small animal models.
Vevo imaging System (VISUALSONICS, Amsterdam, The Netherlands).
Number of animals: 7-9 mice/gender/genotype
Evaluation of the electrical activity of the heart in anesthetized mice.
Experimental reproduction of a cardiac infarction by reversible suturing.
Implantation of a cannula probe to directly measure arterial of ventricular blood pressure in an anesthetized mouse.
Pathological model resulting in average 10% increase in blood pressure but with major fibrosis and left ventricle thickening.
We perform multi-derivation ECG heart in anesthetized mice with 8 probes to generate information about how the electrical activity propagates in 3 dimensions and to determine the electrical axis of the heart. Axis deviations may result from cardiac injury or from a congenital defect.
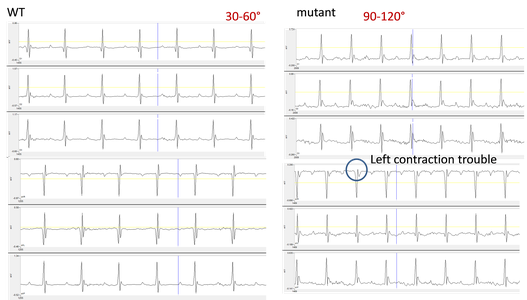
Electrical heart axis difference and specific electrical transmission issues are determined by multiderivational ECG. Multiderivational ECG profiles of a wild-type mouse (left) and mutant mouse (right). Deviated profiles in the mutant animal suggest a left-heart contraction deficiency as well as rotation of the electrical axis to 90-120⁰ from the normal 30-60⁰.
Any strain background can be used
Electrocardiograph ISO DAM8 amplifier (World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, USA) with ECG AUTO v3.3.5.5 (Emka technologies, USA) and 8 lead positions probes.
We recommend 6 mice per group minimum in same anaesthesia conditions and probes positions
Regular forced exercise can create a situation of cardiac hypertrophy. We utilize a swimming regimen in a warm pool over several weeks to induce cardiac hypertrophy.
Telemetry blood pressure and heart rate: continuous recording of the systolic, diastolic and mean blood pressure and heart rate in conscious mice.
Telemetry EKG: continuous recording of electrocardiogram in conscious mice.

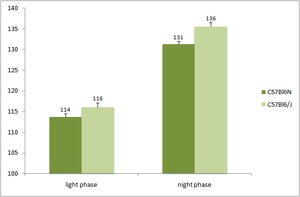
24 channels Data Sciences International acquisition system with 24 RPC-1 telemetric probe
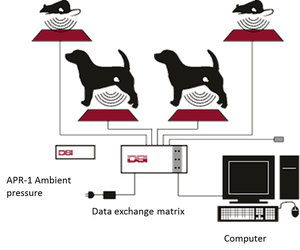
The receiver is the RPC-1 receiver - DSI
-The Data Exchange Matrix - DSI
-The Computer (Dell) - DSI
-The Data Acquisition and Analysis System (Dataquest) - DSI

Telemetry blood pressure and heart rate
The implantable telemetry, PA-C10 Device (transmitter), for blood pressure and heart rate - DSI
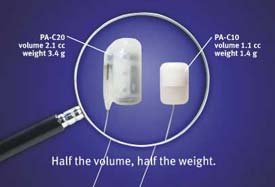

Telemetry EKG
The implantable telemetry devices (transmitters) – DSI ETA-F20 Device for Electrocardiogram

Number of animals: 8-10 mice/gender/genotype
Optimal body weight: 30g
Exploration of airway inflammation and/or airway responsiveness in House Dust Mite-induced lung inflammation.
Advia120
Cytospin 4
Whole-body barometric plethysmograph (EMKA Technologies, Paris, France)
Number of animals - inflammation: 8 mice/gender/genotype
Number of animals - airway responsiveness: 12 mice/gender/genotype
Exploration of airway inflammation and airway responsiveness in LPS-induced inflammation model.
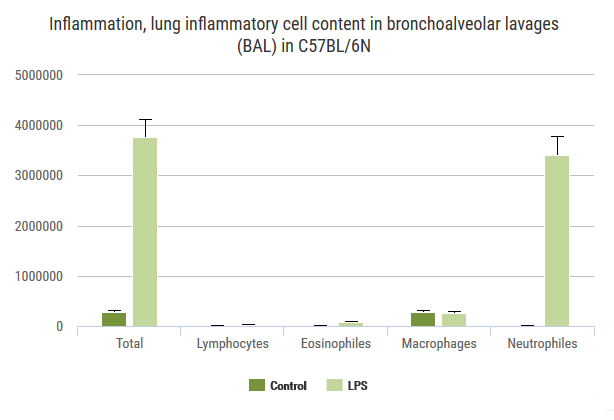
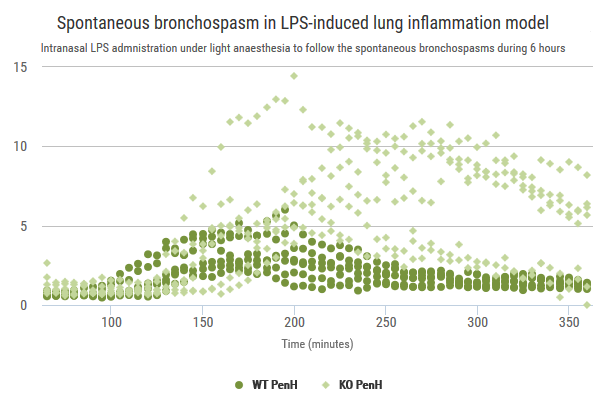
Advia120
Cytospin 4
Whole-body barometric plethysmograph (EMKA Technologies)
Number of animals - inflammation: 8 mice/gender/genotype
Number of animals - airway responsiveness: 12 mice/gender/genotype
We are able to induce eosinophilic inflammation of the lung by presensitizing then exposing the lung to ovalbumin. This can be monitored by whole-body plethysmography, and examined terminally by cytology and cytokine analyses of BALF, immunoglobulin levels in blood and histology.
Use of hypoxia chambers to induce Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) for three of four weeks demonstrates significant resemblance to WHO group III categorized PAH, which includes COPD.
Exposure to chronic hypoxia provides a model of COPD and other PAH disorders in mice. For C57BL/6 mice maintained for 21 days at 0% we see highly significant increases in haematocrit, cardiomyocyte surface area, and right ventricular systolic pressure mimicking human PAH.
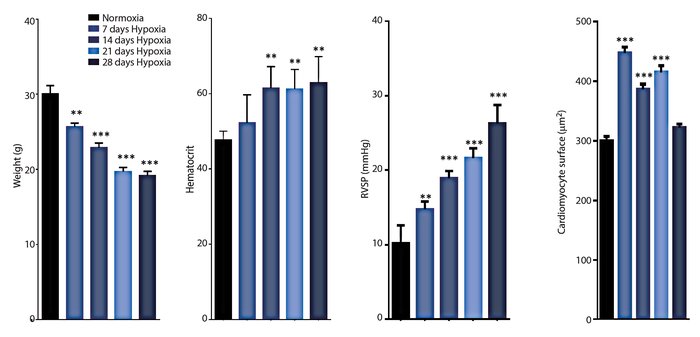
Exposure of C57BL/6N mice to 10% O2 for extended periods resulted in (A) weight loss; (B) increased hematocrit; (C) increase right-ventricular systolic pressure (RSVP); and (D) increased cardiomyocyte surface area.
Pathological model resulting in average 37% increase in blood pressure with small decrease of myocardial relaxation.
Pathological model resulting in average 18% increase in blood pressure with thinkening of arteries and left ventricle.
Pathological model resulting in average 17% increase in blood pressure and some left ventricular hypertrophy.
Determination of systolic blood pressure and heart rate in conscious mice by tail-cuff method.
Two apparatus of BP-2000 seriesII 6 channels (Visitech Systems, Apex, North Carolina, USA)
Number of animals: 9 mice/gender/genotype . Maximum age : 8 weeks
Scan arteries and veins with ultrasound to :
The Vevo 2100 High-Frequency Ultrasound System from Vevo Imaging Systems (VISUALSONICS, Amsterdam, The Netherlands).
Number of animals: 7 mice/gender/genotype/experimental group
Pathological model resulting in average 37% increase in blood pressure with small decrease of myocardial relaxation.
Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis requires 14 days after a single administration to see significant airway fibrosis as well as associated inflammation. Effects are monitored by whole body plethysmography.
Pathological model resulting in average 18% increase in blood pressure with thinkening of arteries and left ventricle.
The intranasal instillation of 3U of elastase is sufficient to establish a meaningful multifocal emphysema in the lungs of mice C57BL6/N after 14 days. This can currently be evaluated by flexiVent™, microCT, and histology.
Exploration of airway inflammation and/or airway responsiveness in House Dust Mite-induced lung inflammation.
Advia120
Cytospin 4
Whole-body barometric plethysmograph (EMKA Technologies, Paris, France)
Number of animals - inflammation: 8 mice/gender/genotype
Number of animals - airway responsiveness: 12 mice/gender/genotype
Experimental reproduction of a cardiac infarction by reversible suturing.
Pathological model resulting in average 10% increase in blood pressure but with major fibrosis and left ventricle thickening.
Pathological model resulting in average 17% increase in blood pressure and some left ventricular hypertrophy.
Exploration of airway inflammation and airway responsiveness in LPS-induced inflammation model.


Advia120
Cytospin 4
Whole-body barometric plethysmograph (EMKA Technologies)
Number of animals - inflammation: 8 mice/gender/genotype
Number of animals - airway responsiveness: 12 mice/gender/genotype
We are able to induce eosinophilic inflammation of the lung by presensitizing then exposing the lung to ovalbumin. This can be monitored by whole-body plethysmography, and examined terminally by cytology and cytokine analyses of BALF, immunoglobulin levels in blood and histology.
Use of hypoxia chambers to induce Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) for three of four weeks demonstrates significant resemblance to WHO group III categorized PAH, which includes COPD.
Exposure to chronic hypoxia provides a model of COPD and other PAH disorders in mice. For C57BL/6 mice maintained for 21 days at 0% we see highly significant increases in haematocrit, cardiomyocyte surface area, and right ventricular systolic pressure mimicking human PAH.

Exposure of C57BL/6N mice to 10% O2 for extended periods resulted in (A) weight loss; (B) increased hematocrit; (C) increase right-ventricular systolic pressure (RSVP); and (D) increased cardiomyocyte surface area.
Regular forced exercise can create a situation of cardiac hypertrophy. We utilize a swimming regimen in a warm pool over several weeks to induce cardiac hypertrophy.